Products
- Ayurvedic tea
- Indian teas
- Supplements
- Oils and drinks for health
- Facial Care
- For Skin
- Dental care
- For personal hygiene
- Sport and Yoga
- For Hair Health
- For massage
- Healthcare
- For Women
- Supplements for Men
- Aromatherapy Essential Oil
- Incense sticks
- Indian Food
- Vegan
- Superfoods
- For meditation
- For home
- New Products
- Specials
- Ayurvedic Herbs
- Wholesale
- Gifts and Kits
Browser notifications:
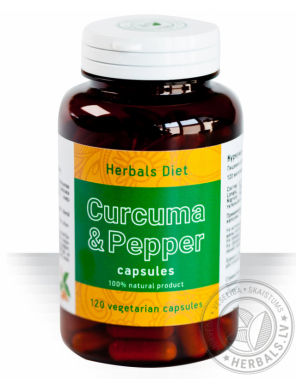
Curcuma& Pepper Herbals Diet capsules
Herbals Diet Curcuma&Pepper capsules
Turmeric is one of the most common ingredient in the Indian cuisine as most dishes are prepared with it.
While curcumin in turmeric has antioxidant, antiseptic, antifungal and anti-inflammatory properties, black pepper has properties that improve digestion, boosts metabolism, regulates nerve signals and controls obesity. Speaking of turmeric and black pepper together, curcumin in turmeric cannot be used properly by our body because of its poor bioavailability. The component's metabolism is pretty quick in the liver and intestinal walls. Only a small fraction of curcumin enters out blood stream. This is where black pepper plays an important role. Black pepper is known to have anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial and antioxidant properties just like turmeric. Piperine is an important and extremely healthy bioactive component which is present in both white and black pepper.
Studies have found that piperine in black pepper improves bioactivity of curcumin in humans. It also improves its concentration in the serum. The best part is that there are no side effects of consuming turmeric and black pepper together. The two ingredients can be used together in various ways.Health benefits of turmeric and black pepper:
Health benefits of turmeric and black pepper:
1. Relieves pain
Anti-inflammatory properties of turmeric have made a superb ingredient that can speed up body's healing process, fight infections and relieve pain. Conditions such as arthritis can also be dealt with by consuming turmeric. Adding black pepper will further intensify the process of relieving pain. Piperine makes the cellular receptors more active and speeds up the anti-reaction process in the body. Chronic and nerve-related pains can also be treated by using turmeric and black pepper together.
2. Reduces inflammation
For years, Ayurveda has recommended turmeric and black pepper for treating inflammation. As mentioned above, both the ingredients have anti-inflammatory properties. Turmeric has often been used to treat, and even prevent arthritis.
3. Manages diabetes
Diabetes is a condition which can cause a possible damage to blood vessels. Researchers say that curcumin and piperine reduces the oxidative stress that damages blood vessels in the first stage.
4. Controls obesity
People on weight loss expedition can use black pepper and turmeric to enhance their process of burning fat and losing weight. Having a mixture of turmeric, black pepper and ginger in warm water early in the morning gives a nice boost to metabolism.
This is possible because curcumin interacts with body's pancreatic, fat, liver and immune system cells. It also takes care of activities such as immune resistance and inflammation. Similarly, black pepper and ginger have a beneficial effect on insulin resistance and fat storage. It reduces both insulin resistance and inflammation. When combined together, the two work wonders for burning excess fat.
Besides piperine, other things which improve bioavailability of curcumin include fat (because it is fat soluble), quercetin (a flavonoid present in citrus fruits like lemon, ginger and even apple Cider Vinegar) and heating.
5. Prevents cancer
It is said that the combination of turmeric and black pepper can prevent risks of cancer. Curcumin plays the role of killing cancerous cells. There have been studies which illustrate the promising nature of turmeric's effect on breast cancer cells, gastric and colon cancer cells and also leukemia cells. Indians consume turmeric on a daily basis. This is probably why the incidence of cancer is low in India as compared to the western countries.
Natural dietary supplement.
Country of origin: Sri Lanka
Manufactured: EU, The trademark Herbal Diet owner - Elfarm Herbalshop
Net content: 120 capsules 700mg. Net weight: 84g.
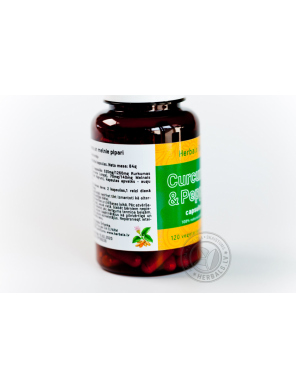
Ingredients 1/2 capsules: 630mg/1260mg Turmeric root powder (Curcuma Longa), 70mg/140mg Black Pepper (Piper Nigrum), vegetarian gelatine.
Information sources:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3834320/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4487614/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15231065
Turmeric is one of the most common ingredient in the Indian cuisine as most dishes are prepared with it.
While curcumin in turmeric has antioxidant, antiseptic, antifungal and anti-inflammatory properties, black pepper has properties that improve digestion, boosts metabolism, regulates nerve signals and controls obesity. Speaking of turmeric and black pepper together, curcumin in turmeric cannot be used properly by our body because of its poor bioavailability. The component's metabolism is pretty quick in the liver and intestinal walls. Only a small fraction of curcumin enters out blood stream. This is where black pepper plays an important role. Black pepper is known to have anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial and antioxidant properties just like turmeric. Piperine is an important and extremely healthy bioactive component which is present in both white and black pepper.
Studies have found that piperine in black pepper improves bioactivity of curcumin in humans. It also improves its concentration in the serum. The best part is that there are no side effects of consuming turmeric and black pepper together. The two ingredients can be used together in various ways.Health benefits of turmeric and black pepper:
Health benefits of turmeric and black pepper:
1. Relieves pain
Anti-inflammatory properties of turmeric have made a superb ingredient that can speed up body's healing process, fight infections and relieve pain. Conditions such as arthritis can also be dealt with by consuming turmeric. Adding black pepper will further intensify the process of relieving pain. Piperine makes the cellular receptors more active and speeds up the anti-reaction process in the body. Chronic and nerve-related pains can also be treated by using turmeric and black pepper together.
2. Reduces inflammation
For years, Ayurveda has recommended turmeric and black pepper for treating inflammation. As mentioned above, both the ingredients have anti-inflammatory properties. Turmeric has often been used to treat, and even prevent arthritis.
3. Manages diabetes
Diabetes is a condition which can cause a possible damage to blood vessels. Researchers say that curcumin and piperine reduces the oxidative stress that damages blood vessels in the first stage.
4. Controls obesity
People on weight loss expedition can use black pepper and turmeric to enhance their process of burning fat and losing weight. Having a mixture of turmeric, black pepper and ginger in warm water early in the morning gives a nice boost to metabolism.
This is possible because curcumin interacts with body's pancreatic, fat, liver and immune system cells. It also takes care of activities such as immune resistance and inflammation. Similarly, black pepper and ginger have a beneficial effect on insulin resistance and fat storage. It reduces both insulin resistance and inflammation. When combined together, the two work wonders for burning excess fat.
Besides piperine, other things which improve bioavailability of curcumin include fat (because it is fat soluble), quercetin (a flavonoid present in citrus fruits like lemon, ginger and even apple Cider Vinegar) and heating.
5. Prevents cancer
It is said that the combination of turmeric and black pepper can prevent risks of cancer. Curcumin plays the role of killing cancerous cells. There have been studies which illustrate the promising nature of turmeric's effect on breast cancer cells, gastric and colon cancer cells and also leukemia cells. Indians consume turmeric on a daily basis. This is probably why the incidence of cancer is low in India as compared to the western countries.
Natural dietary supplement.
Country of origin: Sri Lanka
Manufactured: EU, The trademark Herbal Diet owner - Elfarm Herbalshop
Net content: 120 capsules 700mg. Net weight: 84g.
Ingredients 1/2 capsules: 630mg/1260mg Turmeric root powder (Curcuma Longa), 70mg/140mg Black Pepper (Piper Nigrum), vegetarian gelatine.
Information sources:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3834320/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4487614/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15231065
Also bought
 SPEMAN Himalaya 120 tablets
19.90€
Herbal supplement for the sexual health of men. Improves the quality of sperm
SPEMAN Himalaya 120 tablets
19.90€
Herbal supplement for the sexual health of men. Improves the quality of sperm
 Soria Brewer's Yeast flakes 150g
25.90€
Brewer's yeast flakes
Soria Brewer's Yeast flakes 150g
25.90€
Brewer's yeast flakes
 CURCUMIN MAX LIFELINES veg capsules AKCIJA -70%
4.35€
Triple power: Turmeric extract, Ginger extract, Black pepper extract
CURCUMIN MAX LIFELINES veg capsules AKCIJA -70%
4.35€
Triple power: Turmeric extract, Ginger extract, Black pepper extract
Top sellers
 SPIRULINA ORGANIC Herbals 300 tablets
9.50€
Blue-green algae Spirulina tablets
SPIRULINA ORGANIC Herbals 300 tablets
9.50€
Blue-green algae Spirulina tablets
 MERIT pills
6.50€
Indonesian formula for the reduction and control of body weight
MERIT pills
6.50€
Indonesian formula for the reduction and control of body weight
 BIO TRIPHALA ORGANIC
7.50€
Triphala improves metabolism and has a cleansing and detoxifying effect
BIO TRIPHALA ORGANIC
7.50€
Triphala improves metabolism and has a cleansing and detoxifying effect
This item has been added to cart.